Retinal Photography vs. Dilation: Modern Eye Exams in Tamarac
When you visit your eye doctor for a comprehensive examination, you may encounter two distinct approaches for evaluating the back of your eye: traditional pupil dilation or advanced retinal imaging technology. As healthcare consumers become increasingly informed about their options, understanding these examination methods has never been more important.
Both techniques serve the critical purpose of detecting eye diseases early—often before symptoms appear—but they offer different advantages depending on your individual needs, lifestyle, and health profile. This comprehensive guide examines the science, benefits, and practical considerations of each approach to help you make informed decisions about your eye care.
Understanding Retinal Photography (Digital Retinal Imaging)
Retinal photography represents a significant advancement in eye care technology, utilizing sophisticated digital cameras to capture high-resolution images of your eye’s internal structures. The most widely recognized system is ultra-widefield imaging technology, such as Optomap, which can document up to 82% of the retina in a single capture lasting less than half a second.
The Technology Behind Retinal Imaging
Modern retinal cameras employ multiple laser wavelengths to create detailed, layered images of eye structures:
- Green laser (532 nm): Penetrates the sensory retina and retinal pigment epithelium layers
- Red laser (633 nm): Examines deeper structures from the RPE to the choroid
- Blue laser (488 nm): Enhances color imaging and enables fluorescence photography
- Infrared laser (802 nm): Facilitates specialized angiography procedures
This multi-spectral approach allows eye care professionals to examine different retinal layers simultaneously, providing comprehensive diagnostic information that rivals traditional examination methods.
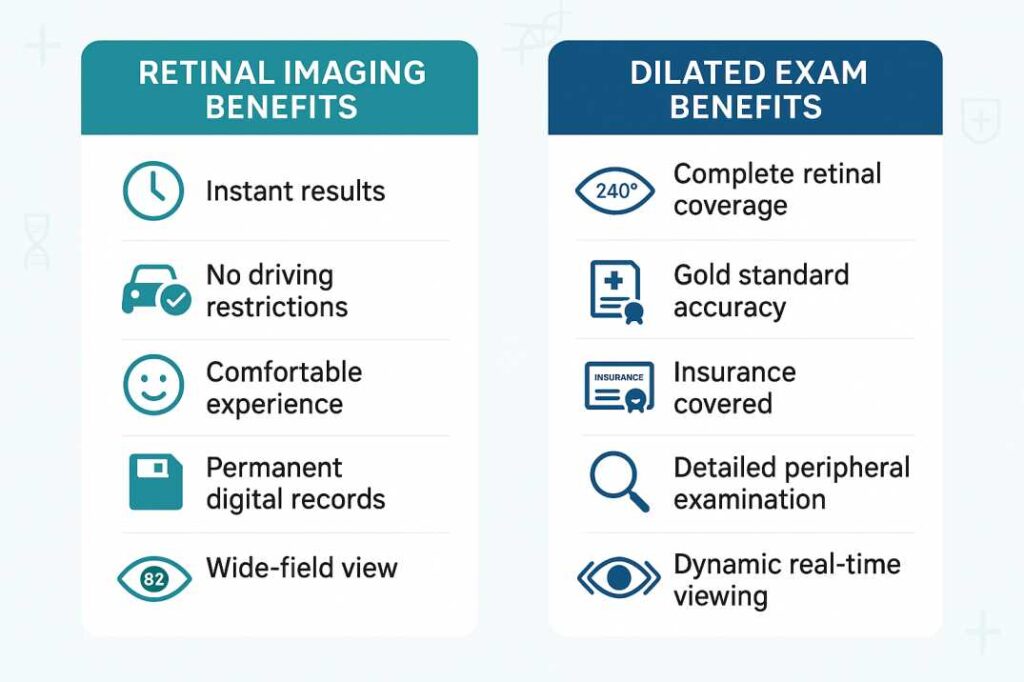
Clinical Advantages of Retinal Photography
Immediate Documentation and Analysis: Digital images are available instantly for review, enabling real-time discussion between doctor and patient. This immediate availability enhances patient education and allows for collaborative treatment planning during the same visit.
Superior Patient Comfort The examination requires no eye drops, eliminates waiting periods, and produces no post-procedure vision effects. Patients can drive immediately after the examination and resume normal activities without restriction.
Comprehensive Field of View Advanced systems capture up to 97% of the retina using auto-montage technology, providing panoramic views that exceed the coverage of many traditional examination techniques.
Long-term Monitoring Capabilities: Images become part of the permanent medical record, enabling precise tracking of retinal changes over time. This longitudinal documentation proves invaluable for monitoring disease progression and treatment effectiveness.
Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy Research demonstrates that retinal imaging can detect subtle changes that might be missed during routine examinations, particularly microaneurysms, small hemorrhages, and early drusen formation associated with macular degeneration.
Comprehensive Analysis of Dilated Eye Examinations
Pupil dilation remains the foundational technique for comprehensive retinal evaluation, having served as the clinical standard for over five decades. This method uses specialized medications to temporarily enlarge the pupils, providing eye care professionals with direct visualization of internal eye structures.
The Dilation Process: Medical Precision
During a dilated examination, topical medications such as tropicamide or cyclopentolate are applied to relax the iris muscles and temporarily paralyze the eye’s focusing mechanism. This pharmacological intervention typically requires 15-30 minutes to achieve full effect and can last 4-6 hours.
Unique Advantages of Dilation
Complete Retinal Coverage Dilation enables examination of up to 240 degrees of the retina, including the far periphery where retinal tears and detachments commonly occur. This comprehensive coverage remains unmatched by current imaging technology.
Dynamic, Real-time Examination. Unlike static imaging, dilation allows for dynamic examination where the doctor can adjust viewing angles, focus on specific areas of concern, and perform detailed stereoscopic evaluation of retinal structures.
Superior Optic Nerve Assessment The three-dimensional view provided through dilated pupils offers optimal evaluation of optic nerve health, crucial for glaucoma diagnosis and monitoring.
Essential for Pediatric Care. In children, dilation remains necessary for accurate refractive measurements, as it temporarily paralyzes the focusing muscle that can interfere with prescription determination.
Insurance Coverage and Accessibility Dilated examinations are universally covered by health insurance plans as part of standard eye care, making this option accessible regardless of financial constraints.
Comparative Analysis: Making the Right Choice
Convenience and Lifestyle Factors
Retinal Imaging Advantages:
- No preparation or recovery time required
- Immediate return to normal activities
- Ideal for busy professionals and parents
- Suitable for patients sensitive to medications
- Comfortable for all ages, including young children
Dilation Advantages:
- No additional cost considerations
- Widely available at all eye care facilities
- Proven track record of clinical effectiveness
- No technology dependencies or equipment limitations
Diagnostic Capabilities Comparison
Detection Accuracy: Recent clinical studies indicate that combining retinal imaging with traditional examination techniques increases lesion detection rates by approximately 30% compared to either method alone. However, each approach offers distinct diagnostic strengths:
Retinal Imaging Excels At:
- Early detection of diabetic retinopathy changes
- Monitoring macular degeneration progression
- Documenting subtle retinal hemorrhages
- Tracking treatment response over time
- Patient education and engagement
Dilation Remains Superior For:
- Peripheral retinal tear detection
- Complete glaucoma evaluation
- Optic nerve assessment
- Emergency eye examinations
- Complex retinal pathology investigation
Economic Considerations
Retinal Imaging Costs:
- Typical fee range: $29-60 per examination
- Usually not covered by vision insurance
- May be covered by medical insurance when medically indicated
- Some practices include imaging in comprehensive exam fees
Dilation Costs:
- Covered by most insurance plans
- No additional patient cost
- Part of a standard comprehensive eye examination
- Universal accessibility regardless of financial status
Evidence-Based Research and Clinical Outcomes
Recent Scientific Developments
Study 1: Enhanced Diabetic Retinopathy Detection (2024) Research published in retinal imaging journals demonstrates that ultra-widefield imaging identifies 19% more diabetic retinopathy cases compared to traditional seven-field photography. When the full 200-degree view was utilized, 15% of cases received higher severity grades, potentially leading to earlier intervention and better outcomes.
Study 2: Comprehensive Lesion Detection Analysis A landmark study from the New England College of Optometry revealed that combining retinal imaging with dilated examination increased overall retinal lesion detection by 30% compared to traditional ophthalmoscopy alone. Detection rates for specific pathologies improved dramatically:
- Drusen detection: 90-100% (image-assisted) vs. 15-62% (traditional alone)
- Small retinal hemorrhages: 95% (image-assisted) vs. 45% (traditional alone)
Study 3: Ultra-Widefield Coverage Validation Current research confirms that modern retinal imaging systems capture 82% of the retina in standard mode, with auto-montage capabilities extending coverage to 97%. Importantly, studies indicate that 66% of retinal pathology occurs beyond the reach of standard fundus cameras, supporting the value of wide-field imaging technology.
Clinical Guidelines and Professional Recommendations
When Retinal Imaging Is Preferred
Ideal Candidates:
- Routine screening in healthy adults
- Patients requiring frequent monitoring (diabetes, hypertension)
- Individuals with dilation contraindications
- Busy professionals with time constraints
- Children who may not cooperate with drops
- Patients requiring detailed documentation for referrals
Clinical Scenarios:
- Annual diabetic retinopathy screening
- Macular degeneration monitoring
- Baseline documentation for new patients
- Insurance or legal documentation requirements
When Dilation Remains Essential
Critical Situations:
- First comprehensive eye examination
- Symptoms of retinal detachment (flashes, floaters, vision changes)
- Glaucoma evaluation and management
- Pediatric refractive assessments
- Complex retinal pathology investigation
- Emergency eye examinations
High-Risk Populations:
- Patients with a family history of retinal disease
- Individuals with diabetes or hypertension
- High myopia patients
- Previous retinal surgery patients
- Those taking medications that affect the retina
Age-Specific Recommendations and Guidelines
Examination Frequency by Demographics
Adults Under 40 (Low Risk):
- Comprehensive exam every 2-3 years
- Retinal imaging is appropriate for routine screening
- Dilation recommended for baseline establishment
Adults 40-64 (Moderate Risk):
- Comprehensive exam every 1-2 years
- A combined approach is often optimal
- Annual dilation for diabetes or hypertension
Adults 65+ (High Risk):
- Annual comprehensive examinations
- Dilation strongly recommended
- Retinal imaging is valuable for monitoring progression
Pediatric Considerations:
- Age-appropriate examination frequency
- Retinal imaging preferred for comfort
- Dilation is necessary for accurate prescriptions
Practical Decision-Making Framework
Questions to Guide Your Choice
Assess Your Risk Profile:
- Do you have diabetes, high blood pressure, or a family history of eye disease?
- Are you experiencing new symptoms (flashes, floaters, vision changes)?
- Is this your first comprehensive eye examination?
- Do you have a history of retinal problems?
Consider Your Lifestyle:
- Do you have important activities planned after your appointment?
- Are you comfortable with temporary vision changes?
- Can someone drive you home if needed?
- Are you sensitive to eye drops or medications?
Evaluate Your Preferences:
- Is cost a significant factor in your decision?
- Do you prefer the most comprehensive examination possible?
- Would you benefit from visual documentation of your eye health?
- Are you interested in tracking changes over time?
Professional Consultation Guidelines
Your eye care professional will consider multiple factors when recommending an examination approach:
- Medical history and current health status
- Previous eye examination findings
- Current symptoms or concerns
- Family history of eye disease
- Age and risk factor assessment
- Lifestyle and scheduling considerations
The Future of Retinal Examination
Emerging Technologies
The field of retinal imaging continues to evolve rapidly, with several promising developments on the horizon:
Artificial Intelligence Integration: AI-powered analysis systems are being developed to automatically detect and classify retinal abnormalities, potentially improving diagnostic accuracy and reducing interpretation time.
Enhanced Imaging Modalities New technologies combining multiple imaging techniques (OCT, autofluorescence, angiography) in a single device promise even more comprehensive retinal evaluation.
Portable and Telemedicine Applications Smartphone-based retinal cameras and telemedicine platforms are expanding access to retinal screening, particularly in underserved communities.
Clinical Practice Evolution
Modern eye care increasingly emphasizes personalized approaches that combine the best aspects of traditional and advanced techniques. This evolution reflects growing recognition that optimal patient care requires flexible, individualized strategies rather than one-size-fits-all approaches.
Special Considerations for Florida Residents
Environmental and Lifestyle Factors
Living in Florida presents unique considerations for eye health that influence examination choices:
UV Exposure Concerns The intense year-round sunlight in Florida increases risks for cataracts and macular degeneration. Both examination methods can detect UV-related retinal damage, but retinal imaging provides superior documentation of progressive changes.
Hurricane Preparedness: Severe weather events can disrupt medical records and prescription availability. Retinal imaging creates permanent digital records that can be crucial if physical documents are lost during storms.
Active Outdoor Lifestyle Florida’s climate encourages outdoor activities that may increase eye injury risks. Regular comprehensive examinations—whether through imaging or dilation—help ensure early detection of trauma-related changes.
Aging Population Demographics: Florida’s significant retiree population requires particular attention to age-related eye diseases. Dilation remains the gold standard for detecting glaucoma and advanced macular degeneration in this demographic.
Professional Recommendations and Best Practices
Integrated Approach to Modern Eye Care
Leading eye care professionals increasingly advocate for individualized examination strategies that leverage the strengths of both technologies. This integrated approach recognizes that optimal patient care requires flexibility and clinical judgment rather than rigid adherence to a single methodology.
For Routine Screening: Retinal imaging provides excellent baseline documentation and patient engagement opportunities, particularly for younger, healthy adults.
For Comprehensive Evaluation: Dilation remains essential for complete assessment, especially in patients with symptoms, risk factors, or complex medical histories.
For Ongoing Monitoring: The combination of both techniques often provides the most comprehensive assessment, particularly for patients with diagnosed eye conditions requiring careful surveillance.
Quality Assurance and Clinical Standards
Regardless of the examination method chosen, several factors ensure optimal care quality:
Professional Expertise The skill and experience of the examining physician remain the most critical factors in accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment recommendations.
Equipment Quality and Maintenance Modern retinal imaging devices require regular calibration and maintenance to ensure diagnostic accuracy.
Comprehensive Assessment Eye examinations should always include multiple components beyond retinal evaluation, including visual acuity, intraocular pressure measurement, and anterior segment assessment.
Follow-up and Continuity: Establishing relationships with qualified eye care professionals ensures appropriate follow-up and coordinated care when needed.
Additional Resources and Clinical References
Professional Guidelines and Standards
1. American Academy of Ophthalmology – Comprehensive Adult Eye Evaluation Preferred Practice Pattern Guidelines. Published in the Ophthalmology journal, these evidence-based guidelines establish professional standards for comprehensive eye examinations, including frequency recommendations based on age, risk factors, and health status.
2. National Eye Institute – Dilated Eye Examination Guidelines Get a Dilated Eye Exam | National Eye Institute Federal health agency guidance providing official recommendations for dilated eye examinations, including procedural information and disease detection capabilities.
3. Clinical Research – Image-Assisted Retinal Examination Comparison of Image-Assisted versus Traditional Fundus Examination Peer-reviewed research published in Eye and Brain demonstrating enhanced lesion detection when retinal imaging is combined with traditional examination methods.
Professional Medical Societies
- American Optometric Association: Clinical practice guidelines for comprehensive eye care
- American Academy of Ophthalmology: Professional standards and continuing education resources
- International Council of Ophthalmology: Global perspectives on eye care best practices
These resources provide evidence-based information supporting the clinical recommendations and guidelines presented in this comprehensive analysis. Healthcare professionals and informed patients are encouraged to consult these authoritative sources for additional technical details and current research developments.
Conclusion
The choice between retinal photography and dilated eye examinations represents a significant decision in modern eye care—one that reflects the broader evolution toward personalized, technology-enhanced healthcare. Both approaches offer distinct advantages, and understanding these differences empowers patients to make informed decisions aligned with their individual needs, preferences, and circumstances.
Retinal imaging technology has revolutionized eye care by providing comfortable, immediate, and highly detailed documentation of retinal health. Its ability to engage patients through visual education and create permanent records for longitudinal monitoring represents significant advances in preventive care.
Dilated examinations continue to serve as the clinical gold standard for comprehensive retinal evaluation, offering unparalleled access to peripheral retinal structures and dynamic assessment capabilities that remain unmatched by current technology.
The future of eye care likely lies not in choosing between these approaches, but in thoughtfully combining them to create individualized examination strategies that optimize both diagnostic accuracy and patient experience. As technology continues to advance and clinical understanding deepens, the integration of traditional expertise with innovative tools promises even better outcomes for patients seeking to preserve their vision throughout their lives.
For patients considering their options: Engage in open dialogue with qualified eye care professionals who can assess your individual risk factors, lifestyle needs, and preferences to recommend the most appropriate examination approach for your circumstances.
For healthcare providers: Stay current with evolving technologies and research while maintaining focus on individualized patient care that combines clinical expertise with appropriate use of available diagnostic tools.
The ultimate goal remains unchanged: early detection and effective management of eye diseases to preserve vision and enhance quality of life. Whether achieved through cutting-edge imaging technology, time-tested clinical techniques, or thoughtful combinations of both, this objective continues to guide the evolution of modern eye care.
This article provides educational information for healthcare consumers and should not replace professional medical consultation. Individuals should consult qualified eye care professionals for personalized examination recommendations and treatment decisions.
FAQs
-
Retinal photography captures digital images of your retina in seconds without eye drops, while dilation uses drops to widen pupils for real-time three-dimensional examination.